

The common base circuit is generally only used in single stage amplifier circuits such as microphone pre-amplifier or radio frequency ( Rƒ ) amplifiers due to its very good high frequency response. Where: Ic/Ie is the current gain, alpha ( α ) and RL/Rin is the resistance gain. The input current flowing into the emitter is quite large as its the sum of both the base current and collector current respectively therefore, the collector current output is less than the emitter current input resulting in a current gain for this type of circuit of “1” (unity) or less, in other words the common base configuration “attenuates” the input signal. The base terminal is grounded or can be connected to some fixed reference voltage point. The input signal is applied between the transistors base and the emitter terminals, while the corresponding output signal is taken from between the base and the collector terminals as shown. Common Collector Configuration – has Current Gain but no Voltage Gain.Īs its name suggests, in the Common Base or grounded base configuration, the BASE connection is common to both the input signal AND the output signal.Common Emitter Configuration – has both Current and Voltage Gain.Common Base Configuration – has Voltage Gain but no Current Gain.Each method of connection responding differently to its input signal within a circuit as the static characteristics of the transistor vary with each circuit arrangement. Bipolar Transistor ConfigurationsĪs the Bipolar Transistor is a three terminal device, there are basically three possible ways to connect it within an electronic circuit with one terminal being common to both the input and output signals. The direction of the arrow always points from the positive P-type region to the negative N-type region for both transistor types, exactly the same as for the standard diode symbol.

The construction and circuit symbols for both the PNP and NPN bipolar transistor are given above with the arrow in the circuit symbol always showing the direction of “conventional current flow” between the base terminal and its emitter terminal. As a small current flowing into the base terminal controls a much larger collector current forming the basis of transistor action. These three terminals are known and labelled as the Emitter ( E ), the Base ( B ) and the Collector ( C ) respectively.īipolar Transistors are current regulating devices that control the amount of current flowing through them from the Emitter to the Collector terminals in proportion to the amount of biasing voltage applied to their base terminal, thus acting like a current-controlled switch.
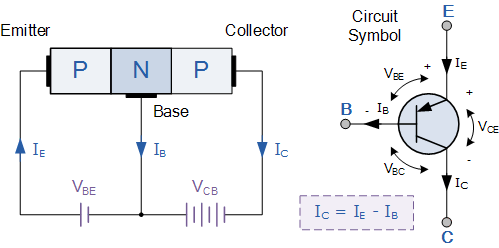
The Bipolar Transistor basic construction consists of two PN-junctions producing three connecting terminals with each terminal being given a name to identify it from the other two. There are two basic types of bipolar transistor construction, PNP and NPN, which basically describes the physical arrangement of the P-type and N-type semiconductor materials from which they are made. The word Transistor is a combination of the two words Transfer Var istor which describes their mode of operation way back in their early days of electronics development.
Bipolar transistor aufbau series#
If we join together two individual signal diodes back-to-back, this will give us two PN-junctions connected together in series which would share a common Positve, (P) or Negative, (N) terminal. The bipolar transistor uses one more layer of semiconductor material to produce a device with properties and characteristics of an amplfier. Unlike semiconductor diodes which are made up from two pieces of semiconductor material to form one simple pn-junction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
